3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we think about creating and producing objects. From complex prototypes to life-saving medical devices, the technology has unlocked a world of possibilities, transforming industries and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Let’s take a closer look at the wonders of 3D printing and how it’s changing the game across various sectors.

What is 3D Printing?
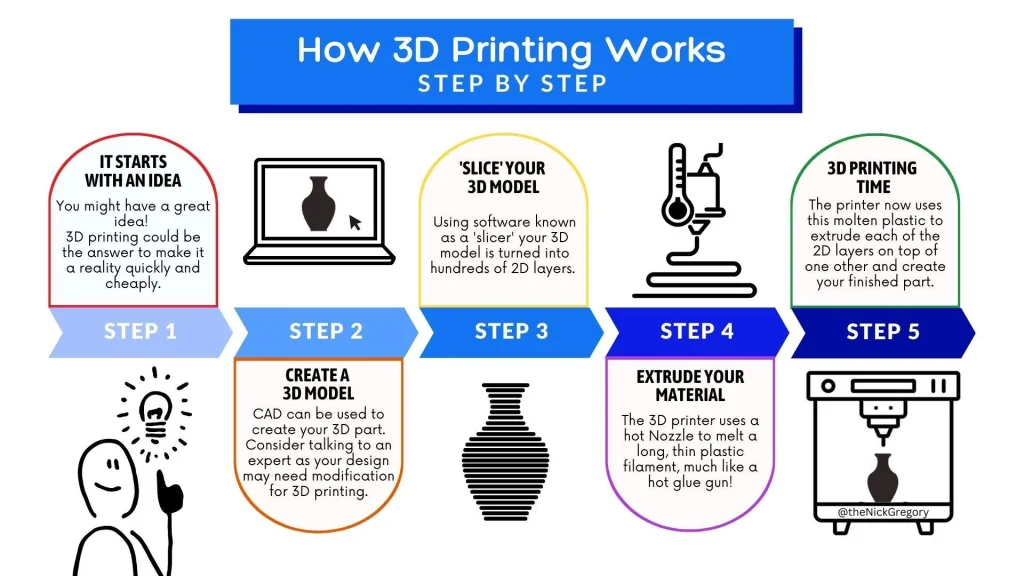
At its core, 3D printing is a process where a digital model is turned into a physical object by adding material layer by layer. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often requires molds or subtracting material from larger pieces, 3D printing offers a far more flexible and efficient way of creating intricate designs. Whether it’s a small item or a massive structure, the process can handle it with precision. The 3D printing process starts with a digital 3D model, which can be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or scanned from a real object. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers, which guide the 3D printer in building the object layer by layer. The printer deposits the material, usually plastic, metal, or resin, in each layer until the final object is complete.
Here’s a basic breakdown of the steps:
Design: Create or download a 3D model.
Slice: The model is sliced into thin layers by slicing software.
Print: The printer builds the object layer by layer, following the sliced instructions.
Finish: After printing, the object may need additional post-processing to smooth surfaces or remove excess material.
Types of 3D Printing
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each suitable for different materials and applications:
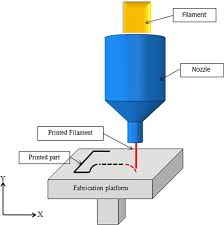
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common type of 3D printing for consumers, where a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded to form the object layer by layer.
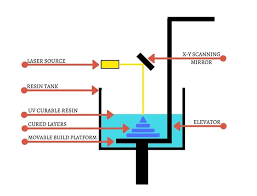
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses liquid resin that is cured with ultraviolet light to build objects. This method produces highly detailed prints.
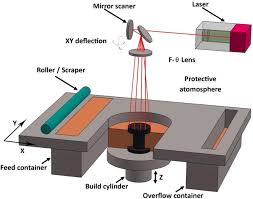
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material (like nylon or metal) into solid structures.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing is used across many industries, from manufacturing and automotive to healthcare and entertainment. Some of its applications include:
Prototyping: Fast and cost-effective prototyping helps designers test and iterate their ideas.
Medical: Custom prosthetics, implants, and even organ models for surgery are being created with 3D printing.
Fashion & Art: Designers use 3D printers to create intricate jewelry, clothing, and art pieces.
Construction: 3D printers are even being used to build houses and infrastructure.
Benefits of 3D Printing
Customization: It allows for the production of custom designs tailored to specific needs.
Reduced Waste: Since material is added layer by layer, 3D printing generates less waste compared to traditional manufacturing.
Cost-Effective for Small Runs: 3D printing is ideal for producing small quantities of complex objects without the need for expensive molds or tools.
Revolutionizing Industries
Healthcare
One of the most exciting applications of 3D printing is in the medical field. From custom prosthetics to personalized implants, 3D printing is helping to create solutions tailored to individual patients. Surgeons can also use 3D-printed models to practice procedures before performing them on patients. In some cases, 3D printers are even used to print tissues and organs, opening up possibilities for advancements in organ transplants.
Manufacturing & Engineering
In industries like aerospace and automotive, 3D printing is revolutionizing prototyping and production. Engineers can quickly create complex parts that would have been expensive or time-consuming to produce using traditional methods. The technology also allows for lighter, stronger materials, improving the performance of products and reducing waste in the manufacturing process.
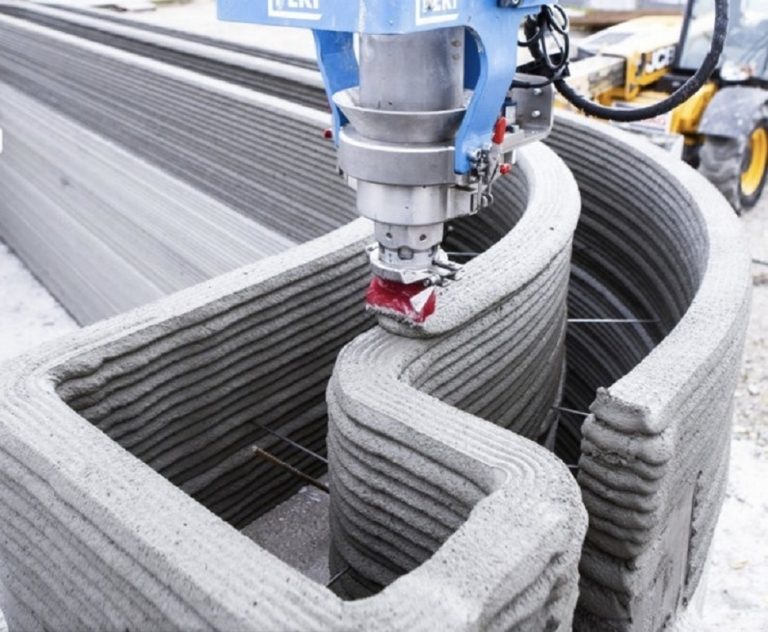
Architecture & Construction
From 3D-printed houses to entire buildings, this technology is making waves in the construction world. With 3D printing, structures can be built faster, more affordably, and with less material waste. It also allows architects to design structures with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional construction methods.
Looking to the future
The potential of 3D printing continues to grow. As the technology advances, we can expect even more incredible innovations, such as 3D-printed food, clothing, and even entire vehicles. The possibilities seem endless, and with ongoing research and development, we are just scratching the surface of what 3D printing can do.
In conclusion, 3D printing is a game-changer, opening up a world of possibilities in industries ranging from healthcare to construction. Its ability to create customized, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions is just the beginning of its wonders. As this technology evolves, it will undoubtedly continue to shape the future of manufacturing, design, and beyond.

